Agriculture, Food & Medicinal Applications
Dicalcium phosphate provides animals with the necessary calcium and phosphorous required in their diets. For similar reasons, it is also added to certain cereals, pet edibles, and can even be bought as a dietary supplement.
Personal Care & Cosmetics
Dicalcium phosphate is useful in the personal care department for its opacity, bulking capabilities, and its ability to affect the overall pH of the product. It can be found used in tooth pastes, deodorants, cosmetic foundations, eye makeup, blushes, and other such types of skin care products.
Dibasic calcium phosphate is mainly used as a dietary supplement in prepared breakfast cereals, dog treats, enriched flour, and noodle products. It is also used as a tableting agent in some pharmaceutical preparations, including some products meant to eliminate body odor. Dibasic calcium phosphate is also found in some dietary calcium supplements. It is used in poultry feed. It is also used in some toothpastes as a tartar control agent.
Dicalcium Phosphate is used as a raw material source of phosphorus in the production of feeds and animal nutrition correctors. With this mineral-sourced phosphate in their rations, the needs of high producing animals are covered, improving performance in growth, fertility and conversion indexes. Phosphorus is essential to, among other processes, ATP formation, nucleic acid synthesis and bone formation.

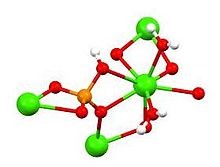

 Simulated body solution (SBF) is a solution with an ion concentration relatively similar to blood plasma, which is prepared under physiological body temperature and pH conditions. This solution was first used by Kokobo and his colleagues to investigate the changes on the surfaces of bioactive glass ceramics. This test is one of the common tests for investigating the bioactivity or biodegradability of biomaterials, and due to the ease of work and the lack of equipment and facilities, it has a wide range and high application, and at the same time, it provides decisive results for researches. has it.
Simulated body solution (SBF) is a solution with an ion concentration relatively similar to blood plasma, which is prepared under physiological body temperature and pH conditions. This solution was first used by Kokobo and his colleagues to investigate the changes on the surfaces of bioactive glass ceramics. This test is one of the common tests for investigating the bioactivity or biodegradability of biomaterials, and due to the ease of work and the lack of equipment and facilities, it has a wide range and high application, and at the same time, it provides decisive results for researches. has it.