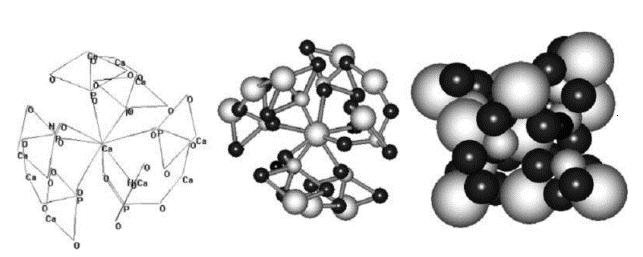
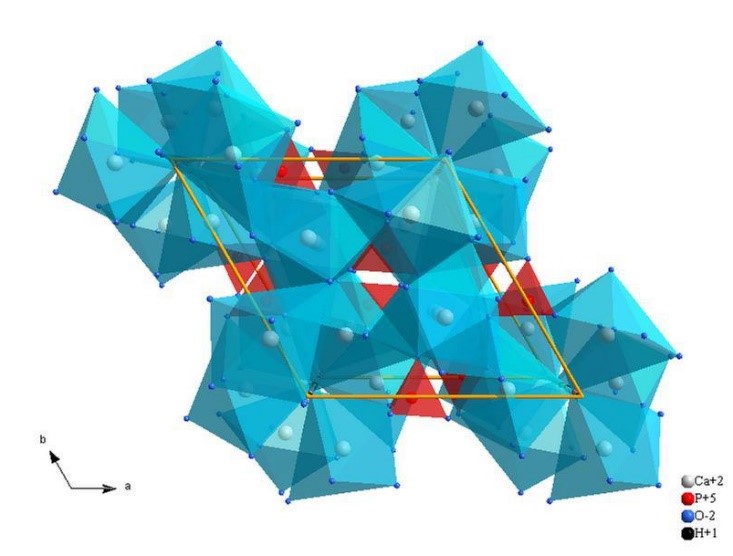
Up to 50% by volume and 70% by weight of human bone is a modified form of hydroxyapatite, known as bone mineral. Carbonated calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite is the main mineral of which dental enamel and dentin are composed. The similar physical and chemical characteristics of natural hydroxyapatite with bone make it biocompatible.
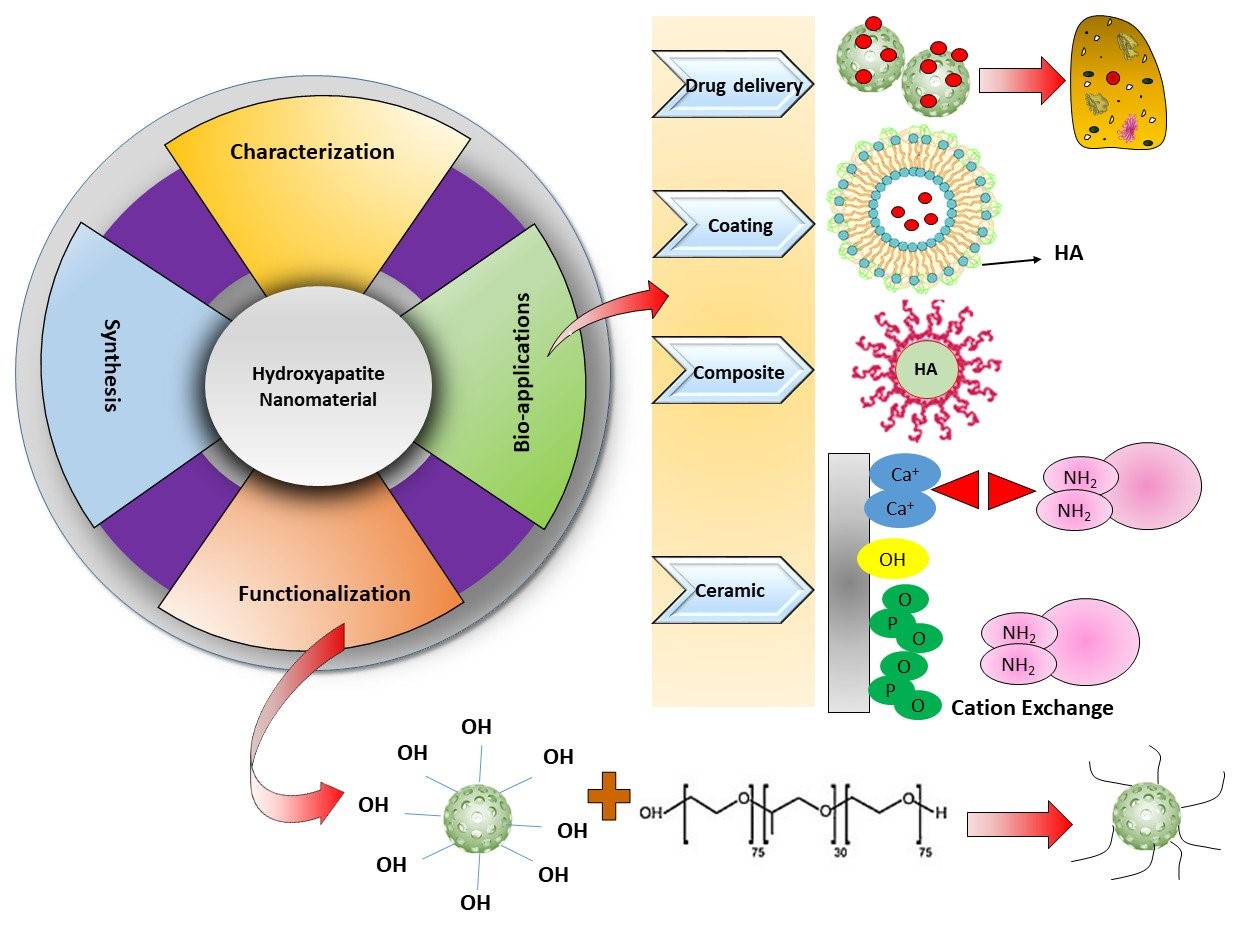
Nano-hydroxyapatite (nano-HAp) is attracting interest as a biomaterial for use in prosthetic applications due to its similarity in size, crystallography and chemical composition with human hard tissue. Bone and teeth enamel are largely composed of a form of this mineral.
An important characteristic of hydroxyapatite is its stability when compared to other calcium phosphates.
Application:
- Among several calcium phosphates, HA is the central complex that resembles chemically and conformationally with bone phosphate complexes. Moreover, hydroxyapatite nanomaterial (HA-NM) is a good carrier for the guided release of substances since it is the most stable calcium phosphate derivative. Therefore, HA has various roles in pharmaceuticals, biomedicine, protein chromatography, water treatment, and fertilizers.
- Calcium phosphate-based ceramics, such as HAP, are of great interest as synthetic bone graft substitutes due to their similarity in composition to bone mineral and bioactivity as well as osteoconductivity.
- Filling dentine tubules and reducing tooth sensitivity
- Restoration of tooth enamel due to the high tendency of this substance to stick to the tooth surface
- Repairing primary dental caries
- Stimulation of skin collagen in rejuvenating creams
- Use in fillers to eliminate skin wrinkles
- The antibacterial properties of nano-hydroxyapatite can be increased by adding silver ions in the HAP structure.