pharmacology industry
Hydroxyapatite (HAP), chemically known as Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, is a biocompatible, osteoconductive, and bioactive ceramic with the ability to form direct bonds with living tissues. Although the use of these inorganic nanoparticles poses controversy regarding its safety, the biodegradability and biocompatibility of HAP are significantly better than other nanoparticles. Compared with polymers, HAP poses a pH-dependent dissolution and a higher biocompatibility. HAP also has higher stability than liposomes and micelles, which tend to dissipate under specific concentrations. Moreover, HAP is soluble and less toxic than SiO2, TiO2, quantum dots, carbon nanotubes, and other magnetic particles.

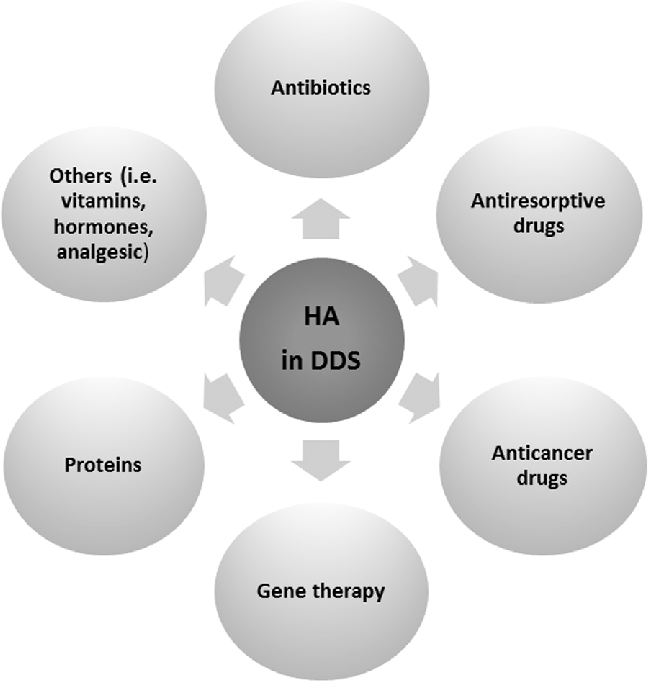
HAP also has a low solubility in physiological pH and is used as a carrier for the local delivery of drugs through surgical placement and injection. For this purpose, three critical forms of HAP can be mainly
used:
- Drugs conjugated or loaded with implanted HAP scaffolds;
- Porous HAP or nano-HAP granular particles;
- Polymer-coated HAP or nano-HAP particles.
Recently, HAP nanoparticles have been used as vehicles for delivery due to their affinity to DNA, proteins, several drugs, and proper release activity. Although there are no conclusions on which HAP nanostructure is more suitable for which kind of molecule, the adsorbed amount is a function of the functional groups interactions, surface area, porosity, pH, and the surrounding medium. the HAP phase while promoting pore formations. However, sintering procedures at higher temperatures makes other phases such as TCP appear due to HAP decomposition.
Zinc oxide has antiseptic and antibacterial properties, so this substance is considered an important competitor for antibiotics in the pharmaceutical industry. Zinc oxide is more commonly known as zinc oxide in the medical and pharmaceutical industries.
It is interesting to know that from a very important point of view, the use of zinc oxide as an antibacterial agent in the medical and pharmaceutical industry is preferable to antibiotics, and that is the issue of creating human pathogens with the use of antibiotics. With the use of antibiotics, the resistance of bacteria to these types of disinfectants increases, and in a way, bacteria update themselves against antibiotic-type disinfectants. In this way, the need to use and increase the dose of antibiotic drugs increases day by day. But this problem does not exist with the use of zinc oxide as a disinfectant, and due to the lack of pathogen production, there is no need to use more or increase the dose of this type of disinfectant.
On the other hand, since zinc oxide is a material with high stability and compatibility, it does not cause problems or damage to the human body and the environment. In addition to the production of disinfectants with high stability and effectiveness, Zno can be used in the production of anti-inflammatory, anti-itching pharmaceuticals, the production of burn ointments, plasters, etc.