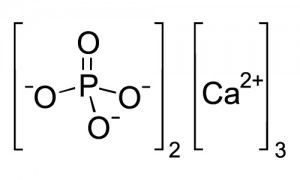
Tricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP) is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate. It is a white solid of low solubility.
Tricalcium phosphate is a supplement form of calcium phosphate and is used to treat or prevent calcium deficiency. Calcium is primarily important for healthy bones and teeth. Calcium is naturally found in foods like dairy, nuts and seeds, and dark, leafy vegetables.
In addition to its use as a supplement, tricalcium phosphate is used as an anti-caking agent in powdered food items. It is also used as an additive in some processed foods to boost calcium content. For those who may need to check the additive status for their country, tricalcium phosphate has E-number E341(iii), a subclass of calcium phosphates. It has a CAS Number of 7758-87-4.
Tricalcium phosphate is an ingredient that is heavily used across many industries – toothpaste, antacids, bone grafting material, baby powder, water filtration, nutritional supplements and ceramic coatings – and it is also in our food supply. Tricalcium phosphate is a mineral found in many foods for many purposes.
Within foods, tricalcium phosphate has roles such as anti-caking, clouding, and fortification. These all support the formulation of more desirable food products in terms of texture, appearance, performance, shelf-life, and nutrition.
Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS), tricalcium phosphate is an ingredient that helps foods, food products and food ingredients live up to consumer expectations time and time again, even after sitting in the pantry or refrigerator after purchase.
Examples of how tricalcium phosphate functions in food manufacturing
• Acidity regulator
• Adds smoothness and opacity to reduced fat foods and beverages, such as soymilk
• Anticaking agent
• Buffer
• Calcium and phosphorus mineral fortification – seen in some juices, soy beverages, yogurts, and cereal products
• Clouding Agent
• Emulsifier
• Firming agent – interacts with gelling agents to strengthen a food structure
• Flour Treatment Agent
• Humectant in some table salts, sugar, or baking powder
• Stabilizer in some fats for frying
• Leavening agent in some baked goods and breadings
• Mineral salt in cheese products
• Thickener
